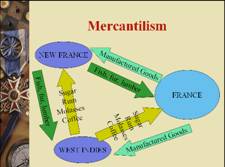
Mercantilism
nThe doctrines of mercantilism protected home markets and
supported exports; tariff policies
discouraged competition from
colonies and foreign rivals.
nBeyond Europe, areas became dependent participants in the world economy as producers and suppliers of low-cost
raw materials; in return they
received European manufactured
items.
nAfrica entered the world network mainly as a slave
supplier.
nEuropeans controlled commercial and shipping services.