Ruling an Empire: State and Church
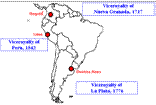
nThe viceroys, high-ranking nobles, represented the king and had extensive legislative, military, and judicial powers.
•The viceroyalties were divided into ten divisions run by
royal magistrates.
•At the local level other magistrates, often accused of
corruption, managed tax and
labor service regulations.
nThe
clergy performed both secular and religious functions.
•They converted
Indians and established Christian villages.
• Some defended Indian rights and studied their
culture.
nThe church profoundly influenced colonial cultural and intellectual life through architecture, printing,, schools,
and universities.
nThe
Inquisition controlled morality and orthodoxy.