I first traveled to Malaysia in 2006, visiting Kuantan on the east coast of Malaysia. Kuantan is a magical place where time moves slowly and the traditions of ancient times are honored and practiced daily. My trip included a Malay Cultural Performance, a traditional wedding ceremony, demonstrations of kite flying, top spinning, and the Art of Batik (a unique way of designing and dying clothing). I also visited a traditional fishing village outside Kuantan. I returned to Malaysia in the Spring of 2015, this time visiting the beautiful capital city of Kuala Lumpur, a vibrant modern city.
|
The region
now known as
|
|
To see the picture album of Malaysia click here

Kuala Lumpur, 2015

Beautiful Kuala Lumpur
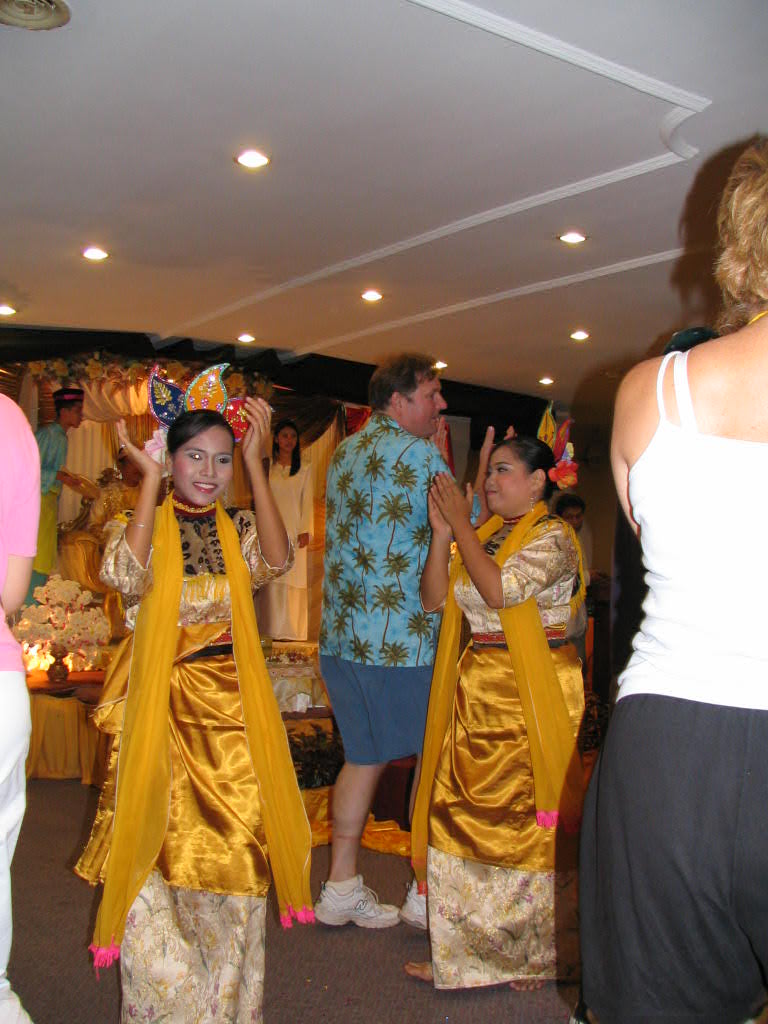

Mr. Stanton "cuts-a-rug" at a Malaysian cultural performance
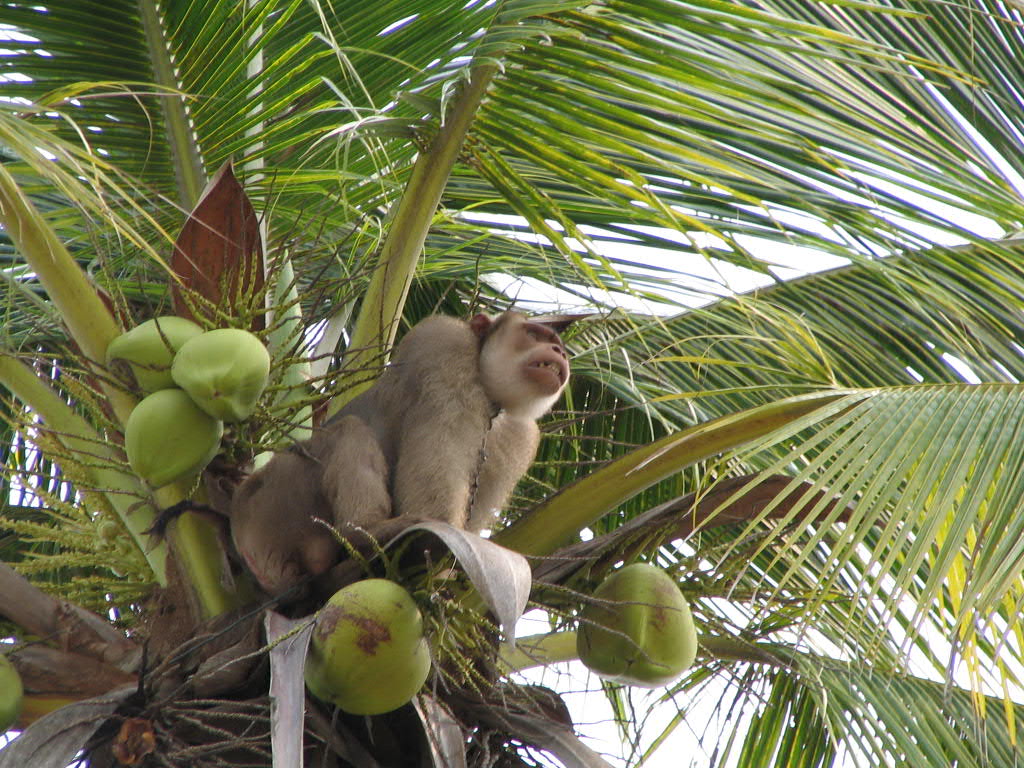

A monkey shows how he retrieves coconuts from a palm tree
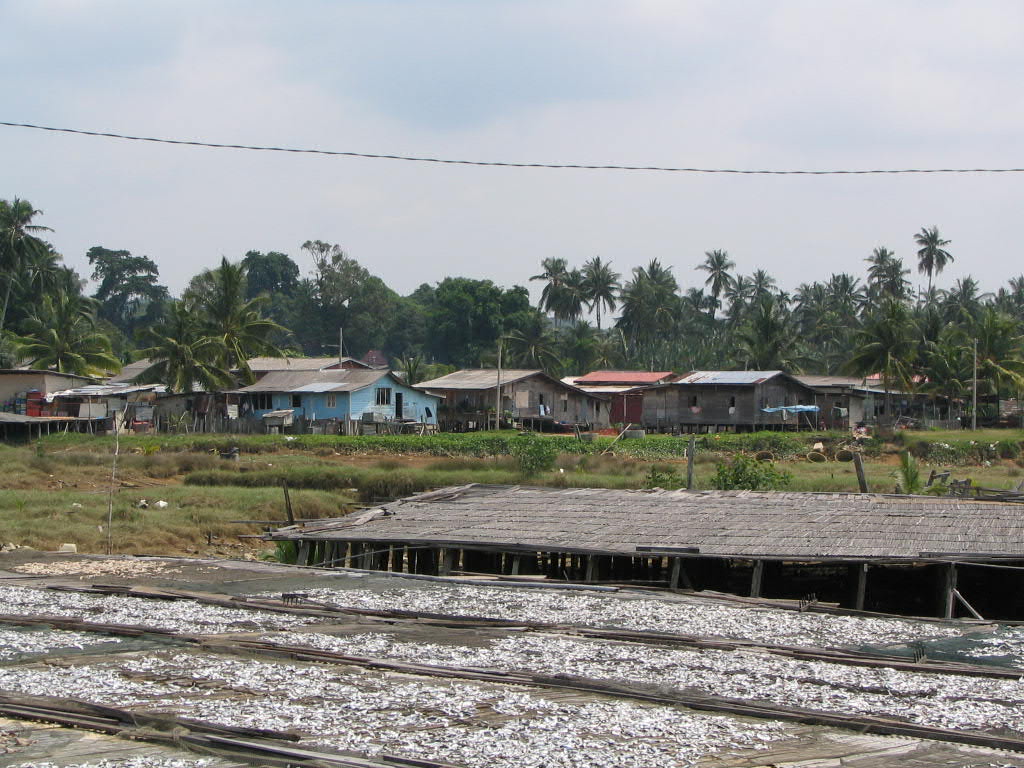

Fish are dried in a fishing village outside Kuantan
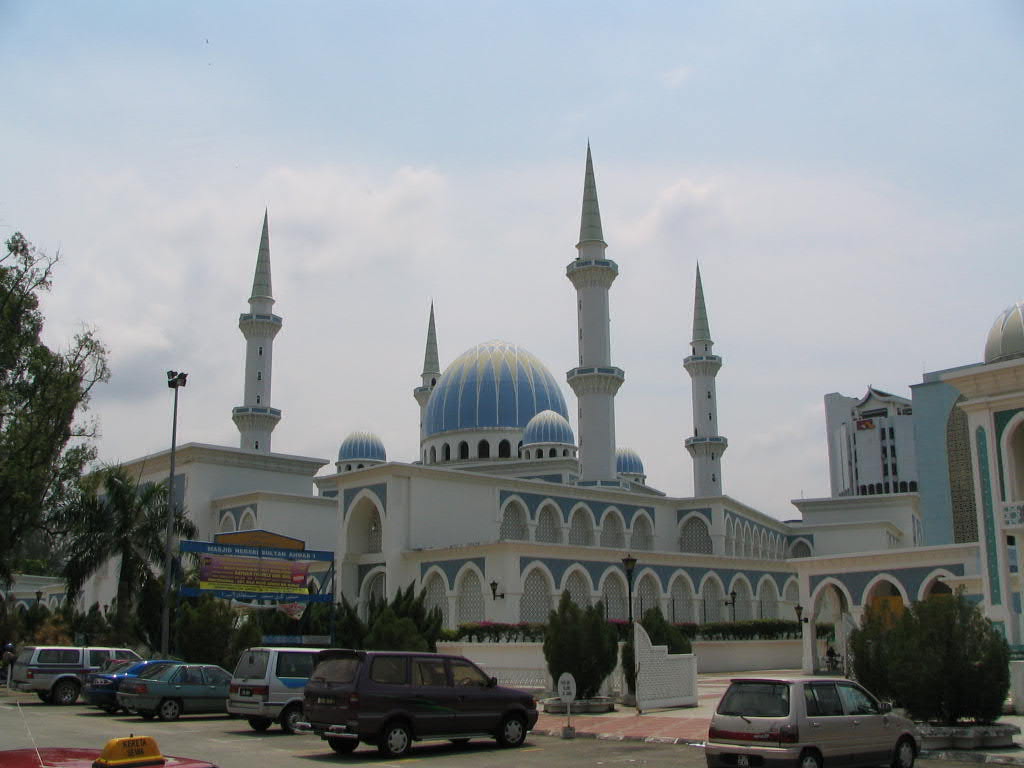

A beautiful Masque in central Kuantan